Although Steven Rauch of Fort Gordon Army Military Base has identified
over 150 events which occurred in Georgia during the American
Revolution, the Georgia Society Sons of the American Revolution focuses
on primarily 8 major battle sites and have produced 8 brochures
concerning these eight "campaigns". The Augusta battle site was really
more than one battle and so was Savannah and Sunbury. In all, most all
of the battles originated as an outcome of the "Southern Strategy"
created by the British beginning in 1778.
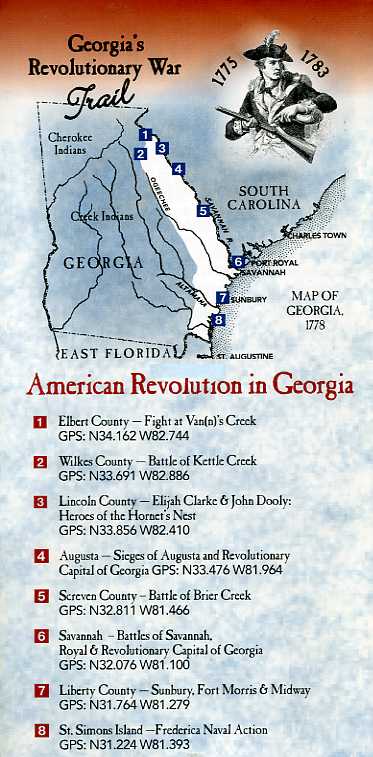
#1- Fight at Van(n)'s Creek - February 11, 1779
(Read More)
(Brochure)
Encouraged by the capture of Savannah, the
British commissioned Loyalist Col. Boyd to raise militia in the Carolina
and Georgia backcountry. With over 700 Loyalists, Boyd attempted to
cross the Savannah River at Cherokee Ford where the
Patriots thwarted his approach. He moved five miles upstream and on
February 11, 1779, crossed at Van(n)'s Creek in present-day Elbert
County. However, Patriot opposition seriously weakened Boyd's forces by
about 100 men, many of whom deserted and returned to the Carolinas. The
Cherokee Ford - Van(n)'s Creek Monument is located at Richard B. Russell
State Park, Elbert County, GA. Telephone (706) 213-2045. GPS: N34.162
W82.744
#2- Battle of Kettle Creek - February 14, 1779
(Read More)
(Brochure)
In early 1779, Patriot Colonels Andrew Pickens, John Dooly and Elijah
Clarke joined forces to overtake Colonel Boyd and his Loyalists. On
February 14, 1779, Boyd halted his troops for breakfast in a flat area
between a steep hill and Kettle Creek. Outnumbered more than two to one,
Pickens attacked with 200 South Carolina Militia in the center, and 160
Wilkes County Georgia Militia on his flanks. Boyd led about 100 men up
the hill where he was mortally wounded. After intense fighting for over
an hour, the Loyalists were routed with a loss of 70 killed or wounded,
and 150 captured. The Battle of Kettle Creek was one of Georgia's most
memorable victories during the American Revolution. The Kettle Creek
Battleground is located 10 miles from Washington off SR 44 in Wilkes
County, GA. An exhibit of artifacts is displayed at the Washington
Historical Museum, Washington, GA. Telephone (706) 678- 2105. GPS:
N33.691 W82.886
#3- Heroes of the Hornetís Nest: Elijah Clarke and John Dooly (Read More)
Two of Georgia's heroes of the American Revolution -- Elijah Clarke and
John Dooly -- rest today on the land where over 230 years ago they
"stung like hornets," routing British, Loyalists and Indians alike. In
addition to the Georgia battles, Clarke and other leaders of the Georgia
Continentals and Militia, including LtCol. Francis Henry Harris, took
decisive roles in the fighting in the Carolinas from May 1780, through
September 1781, while Georgia witnessed a relative lull in the war.
Grave markers of Elijah and Hannah Clarke are located at Elijah Clark
State Park, near John Dooly's home site where Loyalists murdered him.
The Park maintains log cabins, furnished and equipped much like a
Georgia backcountry home of circa 1780. Elijah Clark State Park, Lincoln
County, GA. Telephone (706) 359-3458. GPS: N33.856 W81.466
#4- Augusta in the American Revolution
(Read More)
(Brochure)
A backcountry town of approximately one hundred families, Augusta
was the site of two major battles and was Georgia's Revolutionary
capital after the capture of Savannah.
First Siege of Augusta- On September 14, 1780, Patriot LtCol.
Elijah Clarke led Georgia and South Carolina Militia in an attack on
Loyalist LtCol. Thomas Brown's garrison. Clarke besieged Brown for four
days, but when a British relief force appeared, he had to break off the
siege. Clarke was forced to leave behind many wounded of whom thirteen
were hanged by the Loyalists.
Second Siege of Augusta- During May 1781, Patriot fortunes had
improved in the Carolinas and Continental Maj. Gen. Nathanael Greene
ordered Gen. Andrew Pickens and LtCol. "Light Horse Harry" Lee to join
LtCol. Elijah Clarke in besieging Augusta. In the course of a two-week
battle, Lee's engineers constructed a wooden tower from which a cannon
could reach the interior of the British Fort Cornwallis. Loyalist LtCol.
Thomas Brown held out until June 5, 1781, when he was finally induced to
surrender. The capture of Augusta gave American peace negotiators in
Paris reason to demand the independence of Georgia even though Savannah
remained in British hands for the ensuing year. The Fort Cornwallis
Historical Marker is located behind St. Paul's Episcopal Church,
Augusta, GA. GPS: N33.476 W81.961
#5- Battle of Brier Creek -- March 3, 1779
(Read More)
(Brochure)
In a plan to retake Savannah, Continental Maj. Gen. Benjamin Lincoln
ordered Gen. John Ashe's 1,300 North Carolina Militia to rebuild the
Freeman- Miller Bridge at Brier Creek in current Screven County and
await reinforcements. After capturing Savannah, British Lt. Col.
Archibald Campbell proceeded to Augusta to recruit Loyalists. In
mid-February, he decided to retreat to Hudson's Ferry south of Brier
Creek. Learning that the Patriots were camped at Brier Creek, Campbell
instructed Lt. Col. Mark Prevost with over 1,000 men to proceed
northwestward to Paris Mill, cross Brier Creek and attack Ashe from the
rear. The British skillful maneuver encircling the Patriots, successful
decoy and surprise charge into the Patriots camp ensured the British
victory.
One of the most gallant stands against overwhelming odds during the
Revolutionary War was made by Continental Col. Samuel Elbert. With his
back to Brier Creek and surrounded on the other sides, he attempted to
fight his way through the British lines. Of the 150 Americans killed,
more than half were Elbert`s men. The total rout of the Patriots
re-established Georgia as a Royal Colony until the British were forced
to evacuate Savannah in 1782. The Brier Creek Battle Site is located off
Brannen Bridges Road in the Tuckahoe Wildlife Management Area, in
Screven County, GA. GPS: N32.811 W81.466
#6- Savannah in the American Revolution
(Read More)
(Brochure)
Savannah, Georgia's largest city, was the site of three major
battles and served as Royal and Revolutionary capital.
Battle of the Riceboats- When British warships arrived in the
Savannah River in January 1776, the Whigs placed Governor Wright under
arrest and instructed Col. Lachlan McIntosh to defend the city. During
March 2-7, 1776, British ships took possession of several rice-laden
merchant ships, leading to a heavy exchange of cannon fire with the
Patriots. The British sailed away with the fugitive Royal Governor, and
the Patriots cleared the river of Loyalist raiders.
Capture of Savannah- By 1778, the American Revolution had reached
a stalemate, so the British initiated a "Southern Strategy." Lt.Col.
Archibald Campbell was ordered to invade Georgia, restore British rule,
and prepare for the British capture of other Southern colonies.
Campbell's 3,500 troops landed below Savannah at Brewton's Hill, brushed
away token resistance, and on December 29, 1778, routed the Patriots,
commanded by Continental Gen. Robert Howe. The British lost only seven
men killed and ten wounded, while the Patriots lost 83 men killed and
483 captured. Governor James Wright returned to Savannah in July of
1779, and revived the governments of the Colonial Parishes.
Seige of Savannah- In September 1779, French Count Henri
d'Estaing, arrived off the Georgia coast, and disembarked 4,000 troops
at Beaulieu on the Vernon River. Continental Maj. Gen. Benjamin Lincoln
arrived from Charleston with 1,500 men. On September 16, 1779, d'Estaing
demanded the surrender of Savannah, but 800 Highlanders on a remarkable
forced march through the marsh and swamps, slipped through the blockade
into Savannah. Thus reinforced, British Gen. Augustine Prevost refused
to surrender, and completed his defensive fortifications.
Attack at Spring Hill- The Franco-American attack began early on
October 9, 1779, at the Spring Hill redoubt. British artillery and
musketry ripped the attackers as they advanced. Scottish bagpipes
responded to the French battle cry, "Vive le roi!" British, Loyalist,
and Hessian defenders cut down those who reached the parapet and planted
their colors. The Allied attack failed with the loss of 1,094 killed, of
whom 650 were French. Patriot Gen. Casimir Pulaski, "Father of American
Cavalry," received a mortal wound while conducting a reconnaissance.
Patriot Sgt. William Jasper, hero of the repelled British attack on
Charleston, also received a mortal wound as he defended the South
Carolina standard on the parapet. The British reported a loss of 16
killed and 39 wounded. British Gen. Sir Henry Clinton stated that the
British victory at Savannah was "the greatest event that has happened in
the whole war."
Final Fight for Independence- In January 1782, Continental Maj.
Gen. Nathanael Greene ordered Gen. Anthony Wayne to restore Whig
authority in Georgia and conduct a war of attrition against the British
defenders of Savannah. Wayne established his headquarters at Ebenezer,
and after a series of brutal fights, cut off the British supplies. In a
serious battle at Gibbons' plantation in June, Wayne defeated an attempt
by Creek Chief Guristersigo and 300 warriors to break into Savannah. On
July 11, 1782, the British began to evacuate the city, and Patriot
Lt.Col. James Jackson led his Georgia Legion into Savannah. The last
battle of the Revolution in Georgia took place on July 25, 1782, between
Jackson and British Marines at Delegal's Plantation on Skidaway Island.
The Savannah History Museum includes several Revolutionary War exhibits-
Telephone (912) 238-1779. The Battlefield Memorial Park and Spring Hill
Redoubt is located at the southwest corner of Louisville Road and M.L.
King, Jr. Boulevard, Savannah, GA. GPS: N32.076 W81.100
#7- Sunbury, Fort Morris & Midway
(Read More)
(Brochure)
Siege November 1778- As the British "Southern Strategy" formed,
Gen. Augustin Prevost sent his younger brother, LtCol. Mark Prevost on a
forging expedition against the Liberty County settlements. He also
directed Col. Lewis Fuser through the inland waterways to capture
Sunbury, the second largest town in Georgia. On November 19, 1778,
Prevost crossed the Altamaha River with 750 men, ravaged the
plantations, mortally wounded Patriot Gen. James Screven in an ambush,
and burned the Midway Meeting House. Fuser's naval force of 500 men
occupied Sunbury without firing a shot and he demanded the fort's
surrender on November 25, 1778. Patriot LtCol. John McIntosh, defiantly
replied, "We, Sir, are fighting the battles of America ... as to
surrendering the fort, receive this laconic reply: Come and Take it!"
Fuser refused to attack and returned with his flotilla to British East
Florida.
Capture January 1779- After the British captured Savannah on
December 29, 1778, Continental Gen. Robert Howe ordered Patriot Maj.
Joseph Lane to evacuate Fort Morris. In January of 1779, after failing
to comply with Howe's order, Lane found both Fort Morris and Sunbury
surrounded by over 2,000 British Regulars, Loyalists and Indians. On
January 9, 1779, after a three day siege and a brief heavy bombardment,
Lane surrendered Fort Morris with 24 cannons and large quantities of
provisions. The Patriots lost four killed, seven wounded and about 200
captured, and the British lost one killed and four wounded. Fort Morris
State Historic Site, Georgia's only Revolutionary Historic Site with
earthworks, is located in Liberty County, GA. Telephone (912) 884-5999.
GPS: N31.224 W81.393
#8 - Frederica Naval Action- April 19, 1778
(Read More)
(Brochure)
During 1776 and 1777, four heavily-armed row galleys were constructed in
Savannah for the Georgia Navy, all underwritten by the Continental
Congress. In the Frederica River at St. Simons Island, beginning at dawn
on April 19, 1778, Georgia galleys Lee, Washington, and Bulloch,
commanded by Continental Col. Samuel Elbert, attacked HM brigantine
Hinchinbrook, the armed sloop Rebecca, and a brig. The British attempted
to retaliate, but were out-gunned and out-maneuvered. As they tried to
gain an advantage by moving down river their ships grounded, were
abandoned, and captured. This remarkable victory boosted Patriot morale
and delayed by more than eight months the British invasion of Georgia.
The Georgia Navy Historical Marker is located at the Fort Frederica
National Monument, St. Simons Island, GA. Telephone (912) 638-3639. GPS:
N31.224 W81.393
Prepared by Bill Ramsaur of the Marshes of Glynn Chapter, Georgia
Society Sons of the American Revolution.